- Homepage
- /
- Uncategorized
- /
- Single Phase vs 3 Phase Explained
- Homepage
- /
- Uncategorized
- /
- Single Phase vs 3 Phase Explained
- Homepage
- /
- Uncategorized
- /
- Single Phase vs 3 Phase Explained
Single Phase vs 3 Phase Explained
Are you confused about single phase vs 3 phase power? It’s actually quite simple. In this article we explain the difference between single-phase and 3-phase power, weighing up which option is right for you.
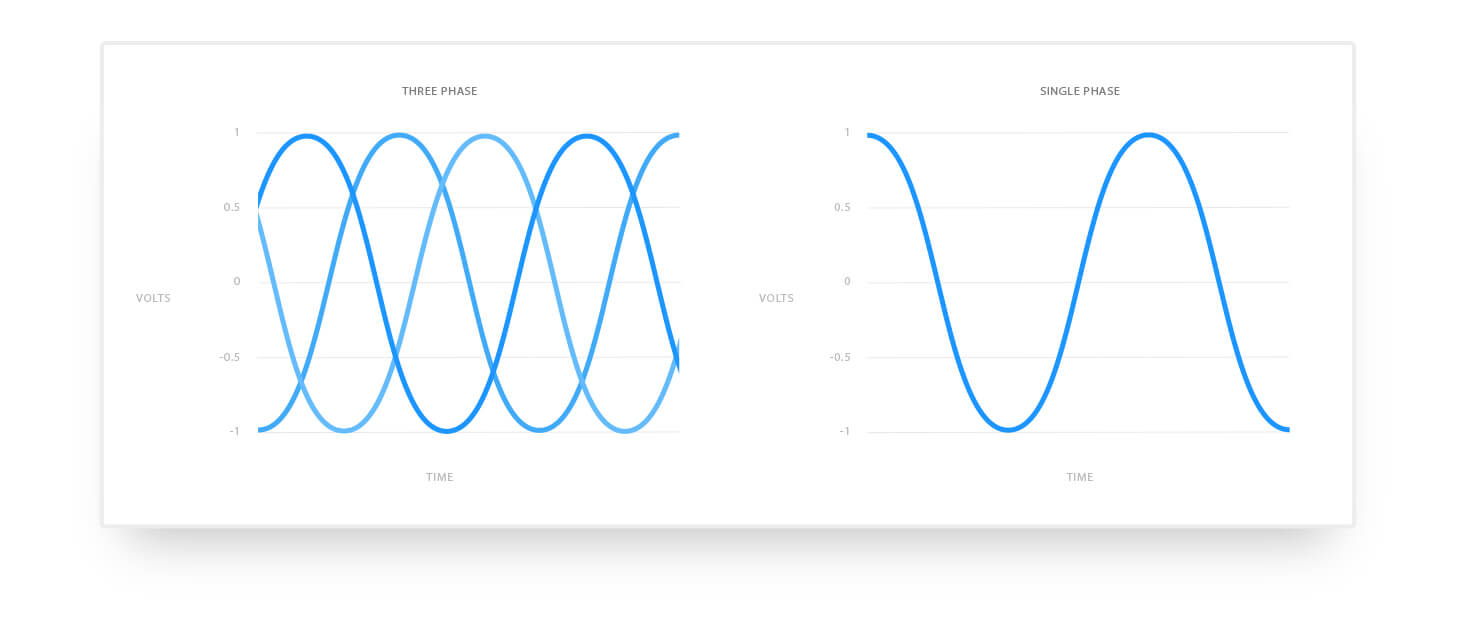
In our homes, plug your device into the wall socket and you’ll be drawing single-phase alternating current (AC). The power in single phase systems isn’t delivered constantly but actually fluctuates. Power is delivered in waves. The wave begins at zero, grows to a peak, decreases to zero, reverses itself where it reaches a maximum in the opposite direction before returning to zero. One complete cycle is 360⁰.
In the UK, the alternating current cycle changes 50 times per second – a frequency of 50hz. In other countries like the USA, the frequency of waves-per-second higher (60hz), which is why you need to buy a step-down transformer to use many foreign electrical devices safely. It may seem complicated, but it’s important to understand how AC works to appreciate the differences between single-phase and 3-phase systems.

What is the difference between single phase vs 3-phase?
In a single-phase system power is supplied through two wires: one delivers the current, the other provides the completes the return path. During one phase cycle power delivery fluctuates, with peaks and dips in voltage. In a single-phase system the power wave peaks at 90⁰ and 270⁰. This means that at two points in a cycle power delivery is at maximum. At other times, the power delivered is less than optimum.
In a 3-phase system, the load is shared across three power wires. The three power wires (A,B and C) are arranged to be out of phase with each other. All three phases of power have entered the cycle by 120⁰. By doing this, the three phases of power peak in voltage at different times during a complete cycle. By supplying power this way there are no peaks and drop-offs. Sharing the load between three wires means power is supplied constantly.
Single-phase and 3-phase compared
The primary differences between single phase vs 3 phase AC are the consistency of power delivery and load capacity. The delivery of power in single-phase systems peaks and dips. Three-phase systems combine alternative currents in varying phases, which ensures that the power delivery never drops below the maximum.
The consistency of power delivery is important for both the safety and security of systems. Any electric circuit has a maximum load – the total amount of amps that it can run before being overloaded. Single-phase power supplies are fine for home use and in some low-consumption commercial applications. They are typically used where the total power requirements are low, often less than 20kVA.
Single-phase systems are actually more efficient than 3-phase systems in low-power applications. They are also simpler to build and engineer. The design of 3-phase systems allows them to safely carry a greater load safely. Typically, 3-Phase systems are used to power high-consumption devices like data centres. The continuous supply of power they deliver is essential for its performance and stability. When power demands are higher, three-phase systems are more efficient – but they are more complex to design. This complexity can come at a cost.
Conclusion
Single-phase and 3-phase power both offer benefits. A single-phase system is perfect for low-demand uses. A 3-phase system is safer for high-demand applications where security and stability are essential.




